Microsoft incorporates PayPal and Stripe with Copilot: Paving the Way for the Future of AI-Powered Commerce
We independently review everything we recommend. When you buy through our links, we may earn a commission which is paid directly to our Australia-based writers, editors, and support staff. Thank you for your support!
Quick Overview
- Microsoft incorporates PayPal and Stripe into its Copilot AI framework to enable effortless transactions.
- This integration signifies a move towards “agentic commerce,” where AI carries out tasks on your behalf.
- Copilot Checkout seeks to enhance online shopping by integrating built-in checkout options within AI dialogues.
- Security is bolstered with the “Agentic Commerce Protocol,” safeguarding your financial information.
- Microsoft’s collaborations with PayPal and Stripe address both consumer and vendor requirements.
- The feature is being launched worldwide, with access in Australia following the US introduction.
- The competition in AI-fueled commerce is intensifying, with players like Google and OpenAI also competing.
PayPal and Stripe Drive the New Copilot Checkout
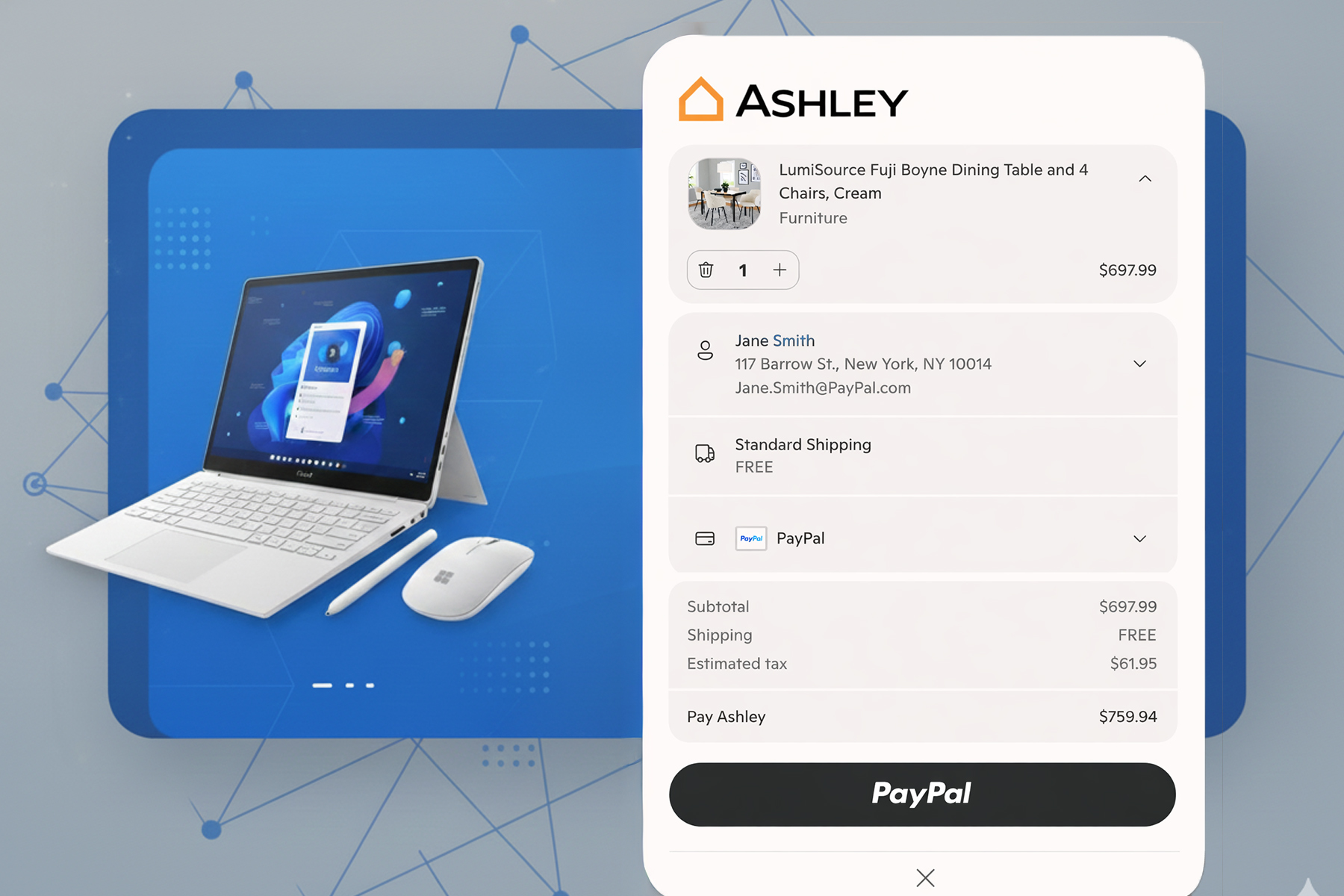
The inclusion of PayPal and Stripe in Microsoft’s Copilot AI ecosystem enables users to make transactions using their existing accounts. This fresh Copilot Checkout experience aims to make online shopping easier by embedding a checkout button directly within AI interactions.
“By integrating PayPal’s reliable payment platform into Copilot, we’re simplifying the process for consumers to transition from discovery to purchase seamlessly.”
Alex Chriss, President and CEO, PayPal.
For users in Australia, systems like PayPal login and Stripe-supported card entry will be available within the Copilot sidebar, guaranteeing secure transactions.
Why Microsoft Requires Both PayPal and Stripe
Microsoft’s alliances with PayPal and Stripe cater to distinct aspects of the e-commerce landscape. PayPal serves as a trusted platform for consumers, while Stripe facilitates backend transactions for enterprises. This dual strategy ensures expansive support for Copilot’s AI-enhanced payments.
“AI is transforming commerce, and as every technology transition requires, new infrastructure is essential. Stripe is developing that infrastructure, and Microsoft is utilizing it by enabling commerce within Copilot.”
Kevin Miller, Head of Payments, Stripe.
Security and the Agentic Commerce Protocol
Prioritizing security, the new “Agentic Commerce Protocol” incorporates a “Shared Payment Token” to safeguard your financial data during transactions, ensuring that the AI does not access sensitive information directly.
How This Alters Your Shopping Experience
Copilot Checkout revolutionizes AI shopping by keeping transactions within the AI interface. This fluid experience promotes increased purchases by removing the need for manual credit card entry, evidenced by Microsoft’s data showing a 53% rise in purchases within 30 minutes of utilizing Copilot.
Availability and Pricing in Australia
Copilot Checkout is initially available in the US, with Australian access on the horizon. This feature comes at no extra charge for both free and Pro versions of Copilot. Microsoft Copilot Pro, available for A$33 monthly in Australia, provides extra features such as enhanced performance.
The Competitive Landscape
With the integration of PayPal and Stripe, Microsoft strengthens its position against competitors like Google and OpenAI, who are also venturing into AI-driven commerce. The success of Copilot will hinge on retailer engagement, especially amongst those using Stripe or Shopify.
Next Steps for Users
Users already with PayPal should link their accounts to Copilot when prompted. It’s also an opportune moment to reassess security settings, including enabling Two-Factor Authentication. As AI commerce develops through 2026, users can anticipate a smoother transition from browsing to buying.
Summary
The integration of PayPal and Stripe into Copilot by Microsoft signifies a pivotal advancement in AI-driven commerce. By optimizing the checkout process and ensuring secure transactions, Microsoft aspires to improve user experience and encourage greater online sales. The anticipated launch in Australia is forthcoming, with competitive ramifications for the expansive AI market.