Quick Overview
- Revolutionary cyclone dust disposal feature eliminates bag usage.
- Noteworthy mapping abilities that require little user involvement.
- Adjustable mop for effective cleaning of corners and edges.
- Smart Agent Hosting Mode learns and adjusts to your home’s cleaning needs.
- Works with Google Home for easy voice commands.
- Offered at a competitive price, particularly during sales.
Appearance
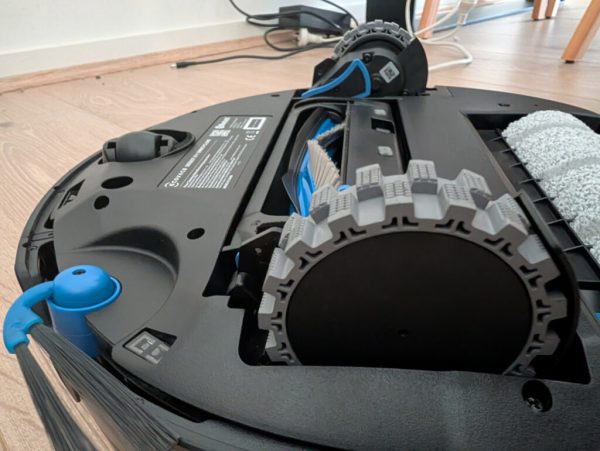
The Ecovacs DEEBOT X11 Omni Cyclone is distinguished by its modern black-grey appearance, which integrates effortlessly into any home environment without being obtrusive. Its design avoids a lidar tower, enabling it to slide under furniture with ease. A control button located on top allows for quick access. The premium construction of the body aligns perfectly with its state-of-the-art features, while the extendable mop provides effective cleaning along walls and corners.
Functionality
The X11 Omni Cyclone thrives in mapping, automatically recognizing surfaces accurately without the need for user adjustments. Its cleaning capabilities leave floors immaculate, regardless if they are wood, tile, or carpet. The robot’s smart battery management ensures it continues cleaning after recharging. Nevertheless, it sometimes has difficulty with bath mats, a potential fix for which may come in future software updates.
Specifications
Cyclone Dust Disposal
This distinctive feature enables the robot to eliminate dust into a container without bags, providing a simple and effective cleaning solution. While some dust may stick to a rubber ring, it can be easily removed.
Adjustable Mop
The adjustable mop addresses the frequent issue of cleaning corners and edges in square or rectangular spaces, ensuring thorough cleaning coverage.
Intelligent Hosting Mode
This mode smartly learns the cleaning needs of your home, adjusting its routine to keep everything tidy without needing user interference. Overrides can be activated for greater control.
Voice Activation
With support for Google Home, users can start cleaning tasks using simple voice commands, enhancing ease of access.
Support for Multiple Floors
For homes with multiple levels, the robot can map various floors and function without a dock, making it a flexible option for larger areas.
Challenges and Possibilities
Even though the bath mat issue is minor, future iterations could enhance the dust-canister design to stop manual dust clearance. Hair tangling on the cleaning roller is another aspect that may be improved, potentially through the introduction of cutting blades or redesigned rollers.
Cost and Availability
The DEEBOT X11 Omni Cyclone can be found at major retailers including JB Hi-Fi, The Good Guys, and Harvey Norman. With a price of $1,987 (down from $2,999), it presents a compelling option, particularly when bundled with accessories or during sales.
- DEEBOT X11 Omni Cyclone: $1,987 (34% discount).
- Accessory Package: $2,063.
- Cleaning solution: two bottles for $75, or a heavy-duty 1L for $37.50.
Conclusion
The Ecovacs DEEBOT X11 Omni Cyclone fulfills its promise of effortless cleaning. Featuring outstanding elements like cyclone dust disposal and smart mapping, it is a significant addition to any household. Despite some minor drawbacks, its performance and pricing render it a competitive option in the robotic vacuum industry, particularly for Australian families in search of convenience.
Recap
The Ecovacs DEEBOT X11 Omni Cyclone sets itself apart with its innovative features and dependable performance. While it has minor imperfections, it provides an appealing solution for those in need of an advanced, easy-to-use robotic vacuum.
Q: What sets the X11 Omni Cyclone apart from other robotic vacuums?
A: Its cyclone dust disposal feature removes the necessity for bags, resulting in a convenient cleaning experience.
Q: How effective is the X11 Omni Cyclone in mapping and cleaning tasks?
A: The robot is proficient in mapping, needing little user interaction, and achieves excellent cleaning outcomes on various surfaces.
Q: Is the X11 Omni Cyclone compatible with voice-activated assistants?
A: Yes, it is compatible with Google Home, enabling users to operate it via voice commands for added ease.
Q: What challenges might arise with the X11 Omni Cyclone?
A: The robot can occasionally have trouble with bath mats, and dust may get stuck in the canister, necessitating manual removal.
Q: Where can I buy the X11 Omni Cyclone, and what is the cost?
A: It is available at JB Hi-Fi, The Good Guys, Harvey Norman, and others, priced at $1,987 with possible discounts.