Ferrari Welcomes Cryptocurrency Through Collaboration with BingX for the 2026 F1 Season
We independently review everything we recommend. When you buy through our links, we may earn a commission which is paid directly to our Australia-based writers, editors, and support staff. Thank you for your support!
Quick Read
- Ferrari collaborates with crypto exchange BingX for the 2026 F1 season.
- Lewis Hamilton joins Ferrari, boosting its market attractiveness.
- Crypto sponsorships are rising in Formula 1.
- Aussie fans can access all races through Kayo Sports and F1 TV Pro.
- The F1 cars in 2026 will focus on sustainability and technological advancements.
A New Chapter for the Prancing Horse
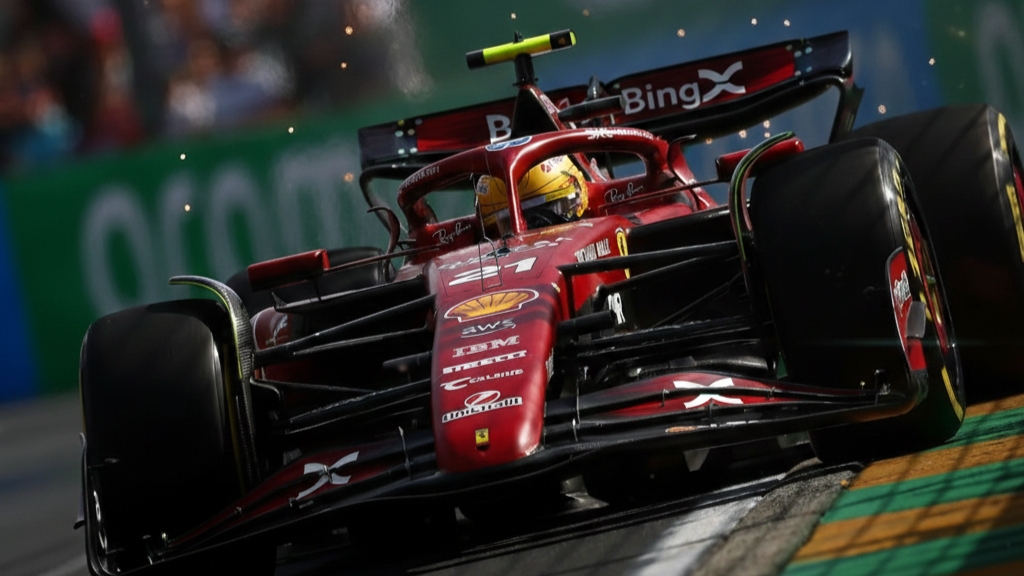
Ferrari, traditionally conservative in Formula 1, is taking a significant step by teaming up with BingX, a leading cryptocurrency exchange. This multi-year collaboration will feature BingX’s logo on Ferrari vehicles, driven by Lewis Hamilton and Charles Leclerc, symbolizing a notable embrace of digital currencies.
Why Crypto and F1 are a Perfect Match
Formula 1 is associated with state-of-the-art technology, making the incorporation of blockchain and data analytics an obvious choice. Fans of the sport generally possess tech-savvy interests, aligning with BingX’s vision of combining the prestige of traditional sports with modern digital finance.
“This collaboration marks a landmark achievement for BingX, as we partner with the most legendary team in Formula 1’s history. It enables us to engage with a worldwide audience of dedicated fans and demonstrate our dedication to innovation and excellence.”Vivien Lin, Chief Product Officer, BingX.
The 2026 Grid is Changing
The 2026 F1 grid is transforming, with technology firms taking the place of conventional sponsors. The new regulations aim to enhance the racing experience, requiring stable, tech-focused partners for teams to navigate expensive developments.
Options and Pricing for Australian Fans
Australian F1 enthusiasts can follow every session through Kayo Sports, starting at A$25 monthly, or choose F1 TV Pro via Foxtel for about A$35 monthly, ensuring full coverage.
The Hamilton Influence
Lewis Hamilton’s transition to Ferrari is a game changer, significantly elevating the team’s commercial standing. His presence, along with BingX’s collaboration, creates a captivating story for the 2026 season.
Digital Assets Gaining Mainstream Recognition
BingX’s branding on Ferrari’s car marks a shift towards mainstream acceptance of digital assets, indicative of regulatory progress. This collaboration is expected to extend beyond mere branding, possibly involving digital fan interactions and blockchain-powered rewards.
Anticipating the Australian Grand Prix
The 2026 season will enthrall Australian fans when it launches at Melbourne’s Albert Park. The BingX branding on Ferrari will be highlighted, emphasizing the strength of new commercial partnerships and technological innovations.
Innovations On and Off the Circuit
The 2026 vehicles will prioritize sustainability, integrating more electrical power and eco-friendly fuels. This aligns with narratives of a digital and sustainable future, positioning tech partners like BingX as key players in this evolution.
Summary
Ferrari’s collaboration with BingX for the 2026 F1 season signifies a pivotal acceptance of cryptocurrency in the sport. With Lewis Hamilton behind the wheel, the team is poised for an exhilarating season both commercially and technologically. The increasing presence of crypto sponsors reflects a transformation in the sport’s funding model, providing Australian fans with various avenues to engage with the exciting 2026 F1 season.
Q: What is the impact of BingX’s partnership with Ferrari on F1?
A:
This alliance integrates cryptocurrency into F1, underscoring the growing acceptance of digital assets and providing a contemporary twist to Ferrari’s classic brand, targeting tech-savvy fans.
Q: How does Lewis Hamilton’s transition to Ferrari affect the team?
A:
Hamilton’s move enhances Ferrari’s commercial attractiveness, drawing high-profile sponsors like BingX and increasing the team’s marketability and fan interaction.
Q: What options do Australian fans have to watch the 2026 F1 season?
A:
Fans can watch via Kayo Sports, starting at A$25/month, or F1 TV Pro through Foxtel for a comprehensive experience at around A$35/month.
Q: What are the updated technical regulations for the 2026 F1 season?
A:
The 2026 regulations emphasize sustainability, with a rise in electrical power and sustainable fuels, in line with the transition to a more digital and environmentally conscious future.