Teenager Sustains Two Fractured Legs in Unlawful E-Bike Collision in Melbourne
We independently review everything we recommend. When you buy through our links, we may earn a commission which is paid directly to our Australia-based writers, editors, and support staff. Thank you for your support!
Brief Overview
- A 17-year-old sustained severe injuries in a prohibited e-bike collision in Melbourne.
- The e-bike, a Surron Ultra Bee X HP, was not legal for road use, and the rider lacked a license.
- Legal repercussions and financial responsibilities await the young rider.
- Victoria enforces stringent laws concerning e-bikes on public thoroughfares.
- Riders are advised to confirm legality and utilize safety equipment to avert accidents.
The Accident
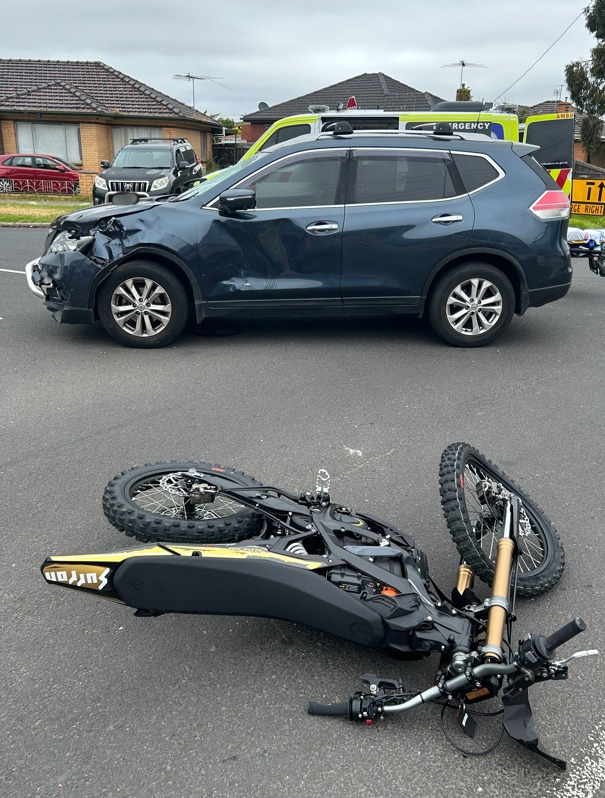
On 9 February 2026, a 17-year-old operating an unauthorized electric motorbike crashed into a vehicle in Altona North, Melbourne. While trying to overtake stopped traffic, the teenager was thrown off his bike when a car turned in his path. He incurred two fractured legs and a dislocated shoulder. This event, regrettably, emphasizes the risks associated with non-compliant e-bikes on public streets.
Legal and Financial Ramifications
The teenager faces serious legal complications, including possible civil lawsuits for damages, as he was unlicensed and operating an unregistered bike. The repair costs for the involved vehicle might exceed A$20,000, creating a burdensome financial obligation. Courts could impose wage deductions or property seizures to resolve these claims.
E-Bike Rules in Victoria
Victoria permits e-bikes on public roads if they meet certain criteria. Pedelecs are limited to a motor power of 250 watts, offering assistance solely while pedaling, and cease assistance at 25 km/h. Throttle-based models must not surpass 200 watts. Bikes exceeding these specifications are categorized as motor vehicles, necessitating registration and licensing.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Riding an illegal e-bike may result in fines exceeding $1,000 for using an unregistered vehicle and about $500 for violating public transport regulations. Victoria Police encourage purchasers to confirm legality prior to buying high-powered e-bikes.
Safety and Accountability
The increase of electric mobility should not compromise safety. Riders are urged to understand local laws and wear suitable safety equipment, including helmets and protective attire, to prevent severe injuries. E-bikes are not toys and must be ridden responsibly on public roads.

Conclusion
The recent incident involving a young individual on an illegal e-bike in Melbourne highlights the importance of adhering to local regulations and safety measures. The situation serves as a vital reminder of the dangers and duties linked with electric mobility, encouraging riders to prioritize safety and compliance.
Q: What are the legal standards for e-bikes in Victoria?
A: E-bikes must have a maximum motor power of 250 watts for pedelecs and 200 watts for throttle-controlled models, along with speed restrictions for motor assistance.
Q: What penalties are imposed for operating an illegal e-bike?
A: Penalties can exceed $1,000 for unregistered vehicle operation and about $500 for breaching public transport regulations.
Q: Who is responsible for damages in a crash involving an illegal e-bike?
A: Typically, the unlicensed rider bears personal liability for any civil claims arising from the accident.
Q: Why is wearing safety gear essential when riding e-bikes?
A: Proper safety equipment, including helmets and protective clothing, can significantly reduce the risk of severe injuries in the event of an accident.
Q: How can one ensure that an e-bike is legal for road use?
A: Check the bike’s compliance with local legislation and consult authorities such as VicRoads prior to making a purchase.
For additional details, visit https://transport.vic.gov.au/getting-around/bicycles/electric-bikes