Snapchat to Introduce Age Verification for Australian Users Starting December 10: Explore the Updated Procedure
We independently review everything we recommend. When you buy through our links, we may earn a commission which is paid directly to our Australia-based writers, editors, and support staff. Thank you for your support!
Quick Read
- A new regulation in Australia mandates age verification for social media sites.
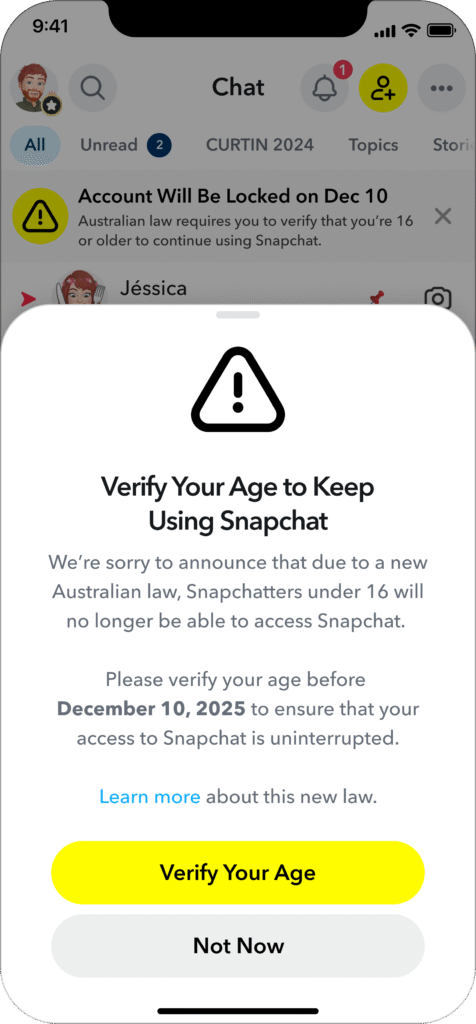
- Users of Snapchat under 16 need to verify their age by December 10 to prevent account lockout.
- Available verification methods consist of ConnectID, a scan of Photo ID, and Facial Age Estimation.
- Non-compliance could lead to a possible three-year account suspension.
- Snapchat opposes the law and calls for more comprehensive privacy-driven solutions.
The Requirement for Age Verification
Australia has introduced the ‘Social Media Minimum Age Act’, which obliges platforms to authenticate the ages of their users. Snapchat, which serves mainly as a visual messaging platform, finds itself in disagreement with this categorization but has committed to compliance as the December 10 deadline nears.
To prepare, Snapchat has begun informing users below the age of 16 through various means, such as in-app notifications, emails, and text messages, regarding the forthcoming adjustments.
Methods of Verification
Snapchat adopts a diverse strategy utilizing third-party services:
- ConnectID (Verified by Banks): Users can authenticate their age through a secure link to an Australian bank account.
- Photo ID Scan: A government-issued identification can be scanned and verified via k-ID.
- Facial Age Estimation: Users can submit a selfie so that k-ID’s algorithm can approximate their age.
The Ramifications of Non-compliance
If age verification is not completed by December 10, accounts will be locked for users under 16, potentially lasting as long as three years. Snapchat is urging affected users to retrieve their data and terminate subscriptions to avoid incurring fees for inaccessible services.
Snapchat expresses disillusionment, perceiving the regulation as an overreach by the government that adversely affects their youngest users. They promote verification at the device or app store level as an alternative.
Snapchat’s Position
A representative conveys the platform’s opinion: “Snapchat is a visual messaging service designed for close friendships. We are disheartened that young Australians will lose connectivity, yet compliance with the law is necessary.”
The Path Forward
For Snapchat users below the age of 16, the directive is straightforward: comply or risk losing access. Snapchat offers assistance for those facing issues with verification or account deactivation. As the deadline approaches, this regulation represents a crucial juncture in Australia’s technological environment, underscoring discussions surrounding digital identity and privacy.
For more information, visit Snapchat.com.
Summary
The Social Media Minimum Age Act requires age verification for users under 16 on platforms such as Snapchat in Australia, effective December 10. Verification methods consist of bank connections, ID scans, and facial recognition, with failure to comply leading to account lockouts. Snapchat contests the classification and champions wider solutions.