Brief Overview
- The Dreame Aqua10 Ultra Track S combines powerful vacuuming with continuous hot water mopping.
- The innovative Track mopping system replaces traditional rotating mop pads.
- With a Vormax suction power of 30,000 Pa, it is one of the most powerful consumer robot vacuums available.
- It boasts an advanced navigation system featuring dual AI cameras and 3D Structured Light.
- Includes ProLeap obstacle navigation and automatic water tank refilling features.
- Priced at $2,999, available at leading Australian retailers.
Design
The Aqua10 Ultra Track S showcases Dreame’s signature sleek, monolithic design, highlighted by an expansive and feature-rich docking station. The robot maintains a classic disc shape, yet its true elegance is found in its mechanics.
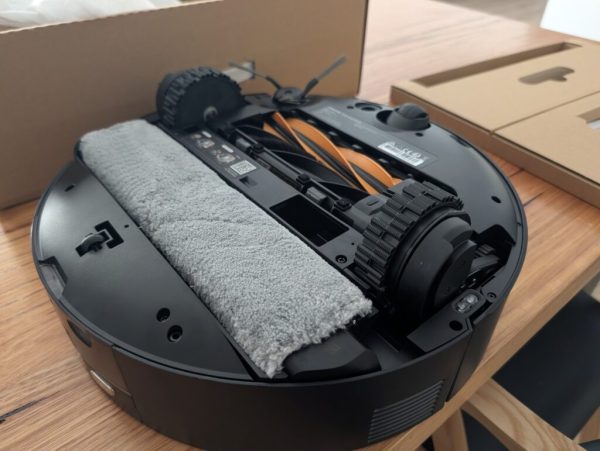
Compared to earlier Dreame models and key rivals, the most notable design evolution is the Track mopping system, which utilizes a wide, always-moistened track mop that replaces the dual-spinning mop heads found in models like the L20 Ultra or the roller mop from the Aqua10 Ultra Roller. This track configuration expands the scrub area significantly and enhances consistency.
The docking station is aptly spacious, accommodating the 4L clean water tank, 3.5L dirty water tank, and the 3.2L dust bag. Although the dock’s dimensions are substantial—420 x 440 x 500mm—it complements the overall design, crafted from high-quality plastic.
The ProLeap system excels by utilizing retractable legs that elevate the robot’s height up to 6cm, enabling it to navigate over high thresholds or thick carpets that often impede other robot vacuums.
This smart design enables it to handle more intricate Australian homes with various flooring transitions. While my home lacks significant height variations, I possess a rug that needs navigating, and the robot adeptly climbs over its edges to ensure the lounge area remains clean.
The only drawback to this excellent capability is the robot’s overall height when the navigation sensor is fully extended, which may still be marginally too tall for the lowest furniture clearances despite the retractable features.
Performance
The primary performance hallmark of the Aqua10 Ultra Track S lies in its robust dual-action cleaning features. The vacuuming function is powered by an impressive 30,000 Pa Vormax suction, among the highest for consumer-grade robot vacuums. This ensures the effortless removal of fine dust, pet hair, and larger debris from both hard surfaces and deep within carpets.
Vacuuming capabilities
The HyperStream Detangling DuoBrush system combines an air-streamed brush for hair and a TPU all-rubber brush for deep-seated dirt, achieving minimal tangling—a considerable advantage for pet owners. In evaluations, it consistently records near-perfect removal rates across diverse debris types on various flooring surfaces and prevents carpet wetness during mopping with its brush lifting feature.
Mopping proficiency
The standout feature is the TrackSync Constant Hot Water Mopping system. It continuously disperses 45°C hot water through 24 nozzles onto the track mop, ensuring constant moisture and heat to dissolve sticky and greasy marks. The combination of enduring heat and intensive down-force mopping pressure scrubs the floors more effectively than conventional wet mopping systems, resulting in a noticeably cleaner finish. The onboard dirty water collection system guarantees that grime is not merely redeposited.
Navigation and obstacle evasion
Featuring the OmniSight System with dual AI cameras and Lateral 3D Structured Light, its navigation capabilities are top-notch. It diligently maps and avoids more than 240 different object types with remarkable accuracy, from small items such as cables and socks to pet waste. The VersaLift Navigation, equipped with a retractable DToF sensor, allows the robot to fit under furniture and subsequently elevate itself to navigate obstacles, highlighting its intelligent adaptability that significantly decreases instances of the robot getting stuck.
Features
The Dreame Aqua10 Ultra Track S is packed with intelligent features that nearly automate every aspect of cleaning and maintenance, providing an effortless user experience.
TrackSync Constant Hot Water Mopping
The first track mop robot vacuum in the world continuously sprays 45°C hot water onto its wide track mop during operation, delivering sustained heat and high-pressure scrubbing to remove tough stains while collecting dirty water in real-time.
ProLeap 6 cm Obstacle Navigation
This advanced mobility system with retractable legs and a three-wheel lifting chassis allows the robot to ascend and overcome obstacles such as double-layer steps and high thresholds up to 6cm, establishing a leading clearance capability.
100°C ThermoHub Mop Self-Cleaning
The docking station utilizes intelligent PTC heating to thoroughly cleanse the track mop with 100°C hot water after each cleaning cycle, effectively breaking down grease and grime, thus maintaining hygiene and preventing unpleasant odours.
30,000 Pa Vormax Suction
A premier suction system that delivers incredibly powerful vacuuming, ensuring deep extraction of dirt and hair from both carpets and hard surfaces, complemented by the HyperStream Detangling DuoBrush to eliminate hair wrap issues.
Up to 100 Days of Auto-Empty
The PowerDock is equipped with a 3.2L dust bag and DualBoost 2.0 automatic emptying technology, allowing debris accumulation to be transferred into the sealed bag automatically for as long as 100 days without manual assistance.
Automatic Water Tank and Solution Refilling
The base station automatically replenishes the robot’s onboard water tank for seamless mopping and automatically dispenses the correct ratio of cleaning solution from its dedicated compartments.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the offered features set a high standard for robotic cleaning, there are several areas for enhancement.
In certain photos, you may notice two units in my possession. This is because the first one encountered a malfunction and was returned for diagnostics. I suspect a failed firmware update, and I genuinely hope customers do not experience this issue. The replacement unit has functioned flawlessly, suggesting the problem may have been singular.
Having experience with robot vacuums over the years, I’m well-acquainted with the initial mapping process for home layouts to enable zone cleaning. I found it necessary for the robot to attempt this mapping a few times to achieve accuracy, and even then, I observed areas that could be improved.
I performed the mapping during Christmas when a tree occupied a corner of the lounge. After removing the tree, I discovered the robot was not cleaning that corner of the room. Instead of adapting to the changes in the environment, it seemed to rigidly adhere to the original map, requiring me to modify the map to address the issue. This functionality could greatly benefit from an automatic adaptation capability for user convenience.
The water tanks are conveniently accessible at the top of the dock, however, they are not as spacious as those found in the Dreame X40 Ultra robot vacuum, which I appreciated for its ability to handle numerous cleaning sessions throughout the week before needing to be emptied or refilled. I would gladly accept a larger dock to achieve this benefit.
Pricing and Availability
The Dreame Aqua10 Ultra Track S robot vacuum cleaner is a high-end product, and its pricing reflects its sophisticated feature set and high level of automation in the Australian market.
The product can be easily found at leading Australian electronics and appliance retailers.
- JB Hi-Fi: $2,999
- Harvey Norman: $2,999
- The Good Guys: $2,999
- Dreame Australia (Official Site): $2,999
It is advisable to watch for promotional periods, as premium robot vacuums in this category typically go on sale, allowing for substantial reductions from the recommended retail price.
In Summary
The Dreame Aqua10 Ultra Track S robot vacuum cleaner is unquestionably a strong competitor in…