Tesla FSD v14 Encounters Its Most Significant Test to Date: A Cross-Country Journey Without Human Assistance
We independently review everything we recommend. When you buy through our links, we may earn a commission which is paid directly to our Australia-based writers, editors, and support staff. Thank you for your support!
“`
Brief Overview
- Tesla’s FSD v14 exhibits its functionalities in a cross-country US journey without human operators.
- The trip acts as a vital evaluation for Tesla’s forthcoming Robotaxi service.
- David Moss’s travels cover around 4,500 kilometers with various updates throughout.
- The successful execution of this expedition may open avenues for self-driving in Australia.
- The FSD system navigates intricate scenarios such as high-speed interchanges and nighttime driving.
Overview
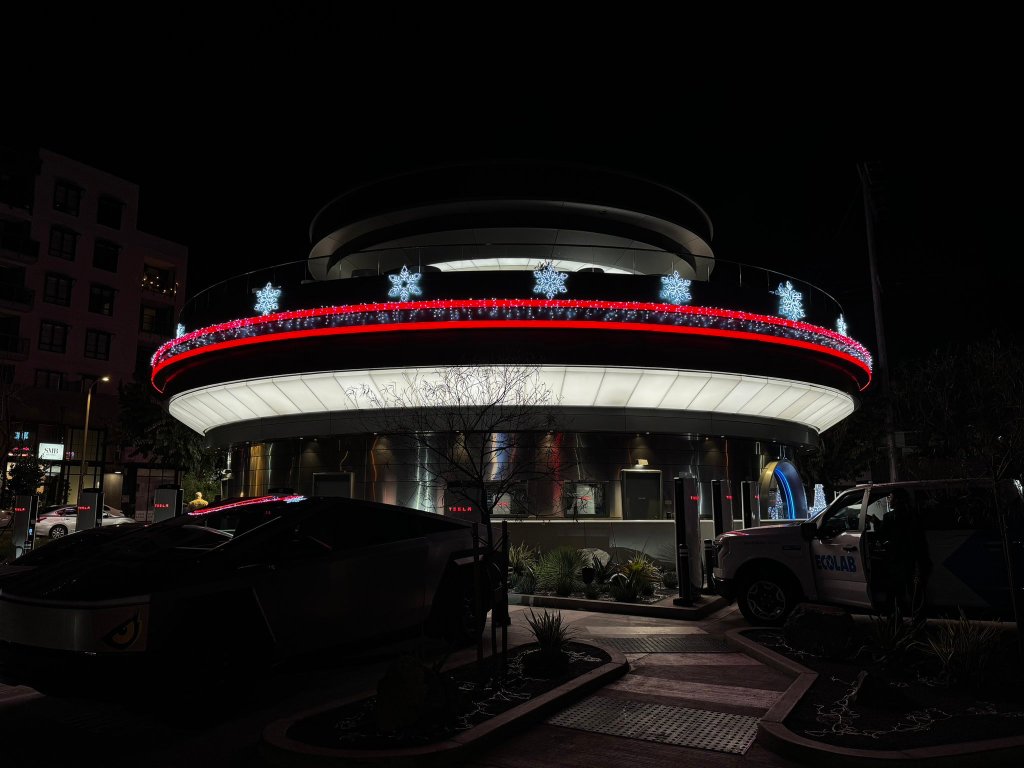
Tesla’s FSD (Full Self-Driving) v14.x is undergoing its most extensive evaluation to date. Tesla owner David Moss is embarking on a cross-country drive across the United States without human assistance. His endeavor is more than just a journey; it marks a pivotal moment in the realm of self-driving.
The Future of Robotaxi
This expedition acts as a demonstration for Tesla’s future Robotaxi service, slated for launch in early 2026. Successfully completing this drive could be transformative, highlighting the software’s capability to traverse various roads and conditions.
Tracking the Path
Beginning in Hollywood, California, David’s journey extends approximately 4,500 kilometers to a beach along the Atlantic Ocean. The voyage is projected to last 45 to 50 hours, factoring in charging pauses.
FSD Cross-Country: The Hollywood Beginning
The journey commenced at the Tesla Diner in Los Angeles, where David activated the FSD software. The initial phase through the heavy traffic of Los Angeles set the groundwork for the challenges to come.
Update Highlights
Mojave Desert
The vehicle showcased its durability by maintaining lane precision amid the high temperatures and heat distortion of the Mojave Desert.
Arizona Border
Upon entering Arizona, the vehicle navigated intricate interchanges effortlessly, reflecting the software’s advancements.
New Mexico Mountain Passes
The FSD system adeptly managed steep inclines and twisting roads, displaying enhanced regenerative braking and decision-making abilities.
The Heart of Texas
While moving through Texas, the system skillfully handled high-speed restrictions and large semi-trucks, providing a more comfortable driving experience.
Night Vision and Human Signals
The upgraded vision encoder excelled in low-light situations, identifying road hazards and responding to human signals.
The Final Leg
As the journey approached its conclusion, the vehicle sustained its performance, leading to a flawless arrival at the Atlantic Ocean.
Implications for Australia
With the Full Self-Driving Capability now available in Australia, the successful completion of this expedition could signify the dawn of autonomous long-distance travel in the country. The technology stands on the cusp of revolutionizing our approach to road travel.
Conclusion
David Moss’s expedition using Tesla’s FSD v14 represents a significant advancement toward achieving complete autonomous driving. The journey not only underscores the software’s potential but also lays the groundwork for future innovations in autonomous travel, including in Australia.
Q: What is the importance of this expedition?
A:
The expedition provides a crucial evaluation of Tesla’s FSD capabilities, essential for the imminent Robotaxi service.
Q: What obstacles did the FSD system encounter?
A:
The system dealt with complex interchanges, high-speed traffic, night journeys, and real-time detours, demonstrating its resilience.
Q: What is the impact on Australia?
A:
It lays the foundation for autonomous driving in Australia, offering a preview of the future of road travel without human involvement.
Q: What advancements were identified in the FSD v14?
A:
Notable advancements encompass improved lane management, immediate obstacle detection, and enhanced night vision functionalities.
Q: What was the distance covered in the journey?
A:
The journey spanned roughly 4,500 kilometers and was estimated to last 45 to 50 hours, inclusive of charging intermissions.
Q: What does the future hold for self-driving technology?
A:
The success of this mission suggests that fully autonomous, long-distance travel is imminent, potentially transforming road transport.
“`