Gozney Reveals the Arc Lite: Space-Saving Pizza Oven Warms Up Compact Areas
We independently review everything we recommend. When you buy through our links, we may earn a commission which is paid directly to our Australia-based writers, editors, and support staff. Thank you for your support!
Brief Overview
- Gozney introduces the Arc Lite, a small, portable pizza oven.
- Created for compact areas like balconies and rooftops in Australia.
- Achieves temperatures of up to 500°C for ideal crusts.
- Weighs a mere 12 kg, facilitating ease of transport.
- Can accommodate a 12-inch pizza on a high-performance stone.
- Now available in Australia for A$649.00.
Gozney’s Innovative Compact Pizza Oven Transforms Small Space Cooking
Gozney, a prominent brand in outdoor cooking, has launched their newest product for the Australian market—the Arc Lite. This small, gas-powered pizza oven is designed to bring professional-quality cooking to limited spaces, such as balconies and rooftops, without sacrificing performance.
Exceptional Performance in a Smaller Package
With a weight of just 12 kg, the Arc Lite is remarkably portable, making it an excellent option for those wanting to enjoy pizza at a friend’s place. Despite its size, it easily holds a 12-inch pizza on a high-performance 12mm stone, ensuring uniform heat distribution for that ideal, airy crust.
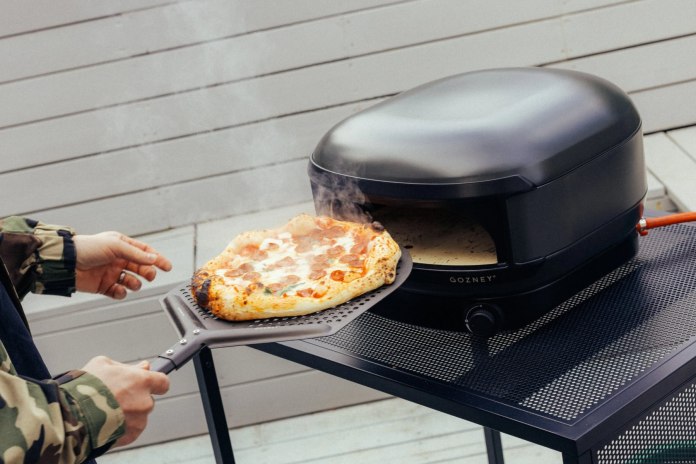

Designed for Simplicity
The Arc Lite is built with user convenience in mind. Featuring a fixed gas connection and an easy-to-use control dial, it streamlines the cooking experience, allowing anyone to handle the flame with ease. Its dual-zone control system enables selection between high and low flame settings for diverse cooking techniques.
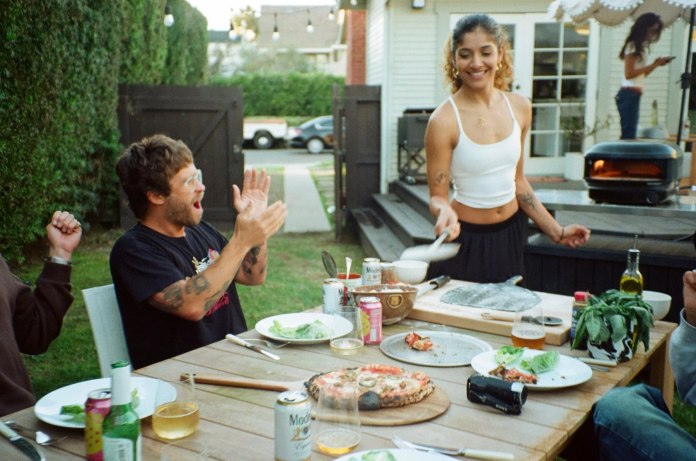

More Than Just a Pizza Oven
While pizza is the main attraction, the Arc Lite excels at cooking a variety of dishes as well. Its lateral flame design is ideal for roasting both vegetables and meats, providing a versatile outdoor cooking environment. The fully insulated body guarantees thermal efficiency, ensuring steady performance even in windy conditions.
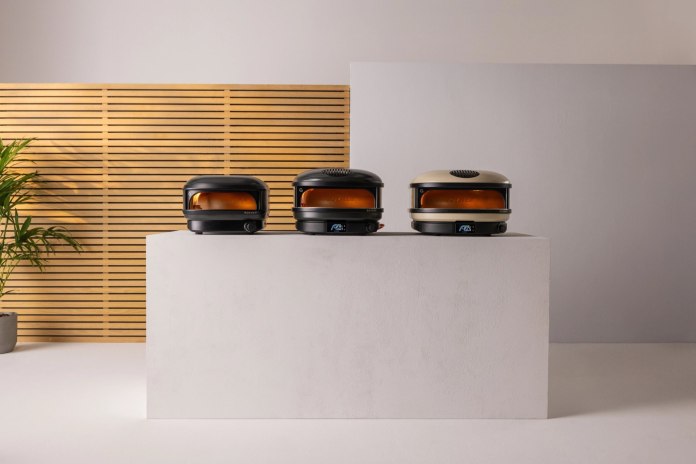

Pricing and Local Availability
Offered in a sleek Off Black finish, the Arc Lite is currently available in Australia for A$649.00. It can be ordered from the Gozney website or select local stores, providing an accessible option for high-end outdoor cooking.
Enhance Your Experience with the Right Accessories
Improve your Arc Lite experience with Gozney’s specialized accessories. The Venture Placement Peel and Venture Turning Peel are crafted for the oven’s compact entrance. Moreover, a weatherproof cover is available for A$59.00, safeguarding the unit from outdoor elements. The oven is backed by a standard 1-year warranty, which can be extended to 5 years with registration.
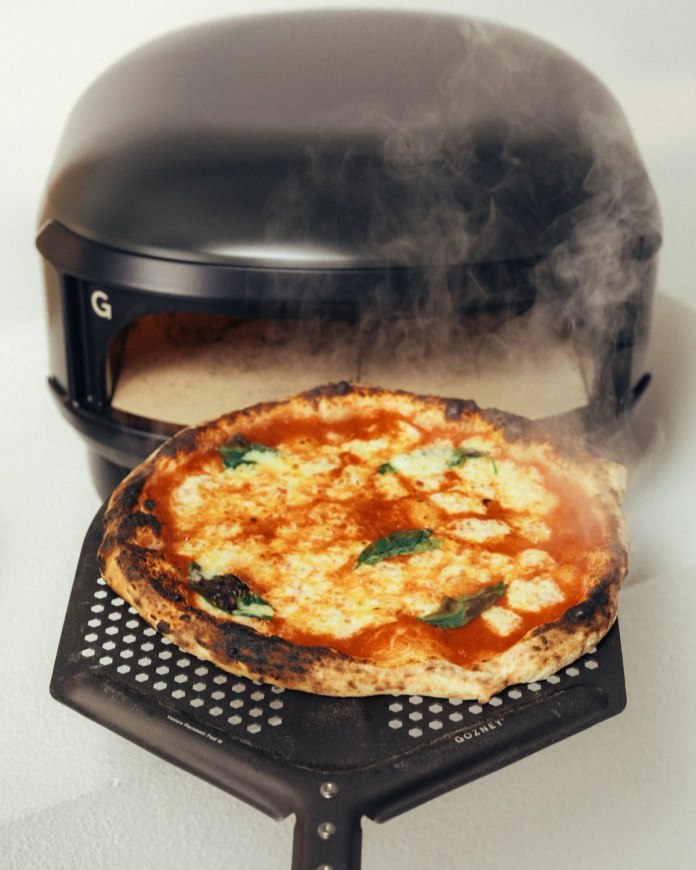

Concluding Remarks
Gozney’s Arc Lite is a revolutionary product for those with limited space or budgets. Providing an authentic taste of professional live-fire cooking, it is ideal for city residents looking to enhance their outdoor gatherings. With the Arc Lite, anyone can craft the perfect pizza at home without requiring a large outdoor area.
Recap
The Arc Lite from Gozney is a compact, high-efficiency pizza oven made for small areas. It provides flexibility and simplicity, making it a great choice for anyone aiming to upgrade their home culinary skills. Priced at A$649.00 in Australia, it delivers a premium cooking experience without the need for large space requirements.